Deformation of foot valgus is most often congenital. However, in some cases - with paralysis, traumatic lesions - may appear during a mature life. The main symptoms of the pathology are pain in the foot and lower muscles, visible violations of the foot, as well as changes in walking. Diagnosis of the disease is performed using clinical examination, X -Ray, electromilography, and others. Treatment includes conservative and surgical methods. However, proper efficacy is only observed in reconstructive operations.
What is this disease?
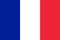
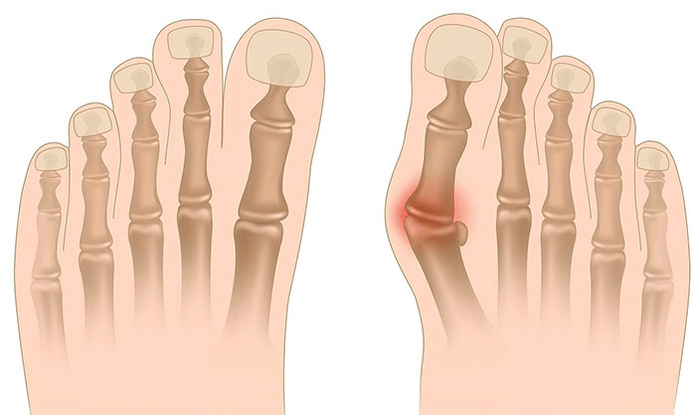
Deformation of valgus is a curvature of the foot, characterized by a longitudinal gate compaction. Usually, the inner edge of the leg is lowered ("drops"), and the heel is apparently.
A person's feet, based on their location, take pressure on the whole mass of the human body. For this reason, it has a special anatomical structure, which allows for depreciation, balances and stabilizing movement. However, the important component for the execution of these tasks is the correct form of stop.
Today, the most important traumatological and orthopedic problem is the deformation of the foot valgus. The meeting was estimated at 30-58%, where 2/3 cases form congenital disorders.
This pathology is largely important social, as it covers all population age groups, and also helps to complement spinal columns, early development of osteochondrosis and joint arthrosis of the lower leg.
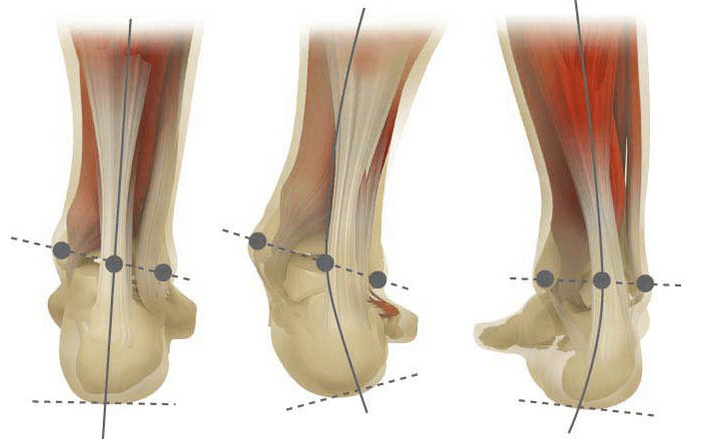
When you take your feet (if you look at it from behind), deformation like X is formed at the ankle level: the ankle is in contact, while the heel is 5-6 centimeters from each other.
Often, the pathology is congenital and diagnosed with the children returning to the hospital (or immediately after the beginning). The same situation is adjusted for up to 5 years, after which (without proper treatment), a child develops a flat leg.
Why does it come from?
It is believed that the main cause of the appearance of deformation of the foot valgus is an inadequate function of the posterior tibial muscle or weakness of the ligament.
Today, other factors in pathological development are distinguished:
- Congenital abnormalities with improper locations of the bones or shortening of tendons (vertical ram bones, short pile tendons);
- Posture disorders when deformation of the foot offset the curvature of the spinal column;
- Traumatic lesions (bone fractures, lower legs, hips or knees, ligaments and tendons);
- Paralysis (immobilization) due to damage to the nervous system for encephalitis, polyomyelitis, stroke, cerebrospinal liquid violation for hernia, and so on;
- Cramps (persistent contraction) of lower leg muscles;
- Disease equivalent: pathology of bone system with vitamin D (rickets), diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis (reduced bone density), impaired thyroid gland and parathyroid, and so on;
- Weight loss, including weight gain in menopause or during pregnancy.
The development of pathology is also facilitated by the wrong selected shoes or the excess club correction in the childhood.
Degree and level of illness
Pathological severity (power of manifestation) is divided by degrees:
- Light with the height of the vault 1. 5-2 centimeters and the angle of the heel tendency to 15 degrees;
- Flat -Rata, when the gate is flattened to a centimeter 1, and the angle decreases to 10 degrees;
- Weight at the height of the vault up to 0. 5 cm and the angle of the heel tendency is 5 degrees.
Depending on the involvement of a particular structure, the following levels of curvature are distinguished:
- No deformation of the bone, the pain is determined on the inner surface of the ankle (in the posterior muscle muscle binding area);
- Curvature is light, the heel is slightly rejected;
- The feet are allocated, and the deformation is fixed (not correctly corrected);
- Wending is observed not only on the feet, but also in the ankle joint.
Symptom
In the first stage, the patient is interrupted by periodic pain after walking or long vertical load (standing or sitting on the foot). As a rule, the pain syndrome is increasing as it walks in the shoes that are not selected. The next stage of the disease is associated with the occurrence of foot curvature: the patient in the standing position does not depend on the outer edge of the foot, but with the entire area. A little change in walking style.
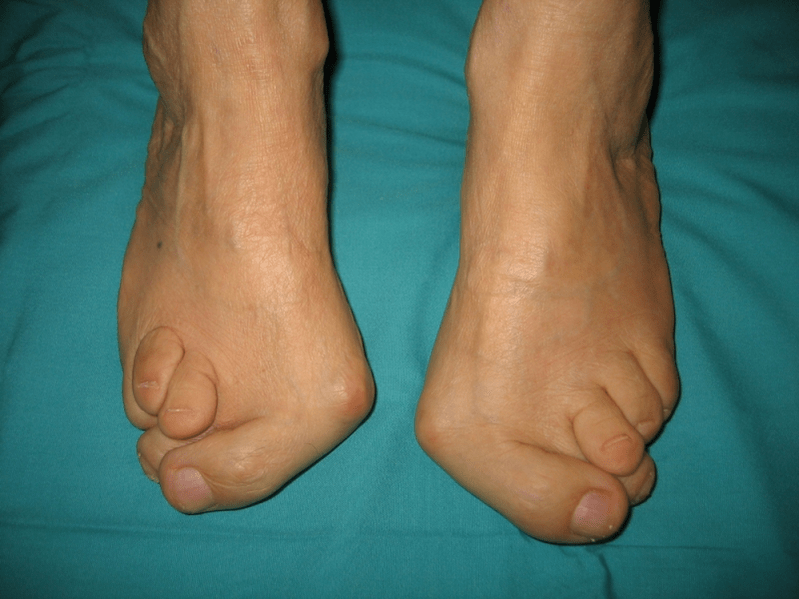
In the third stage, the melted bone higher is determined (feeling lower than the ankle on the inner surface of the ankle), as well as the strong removal of the heel outside (the patient stands based on the inner edge of the heel). The deformation of the advanced valgus foot is characterized by clear curvature from both feet itself and ankle joints. Patients complain of severe pain in the lower leg muscles, as well as significant gait violations: knees rubbing each other, while the right and left legs are located at certain distances.
Severe foot curvature is often complicated by deformation of the spinal column (scoliosis with different positions of the shoulder and pelvic wing), osteochondrosis (damage to the intervertebral disc with the formation of hernia) or arthrosis (intraarticular cartilage).
How to diagnose?
The diagnosis of foot curvature consists of:
- Clinical examination, in which orthopedis detects decreases in the leg gate, heel deviation and ram bone, "loss" that appears outside and the prominence of the ankle.
- X -Ray - an affordable and informative method in which you can determine changes in the angle of bone tendency and linear parameters of their relationship. These indicators are needed to make the final diagnosis and explain the level of deformation.
- Methods of registering steps aimed at determining the exact functioning of the body. This method consists of registering the support time of the individual part of the foot during the steps. During the course of the study, the foot rolling phase was also studied, which reflects the muscle balance of the lower limbs.
- Dynamic electromyography, which records the electrical activity of the muscle studied and its dependence on the step phase.
- Photossmography with digital processing that allows you to obtain all standard indicators and determine the type/degree of curvature with high accuracy.
Additional consultation of neurologists (by deformation due to cramps or paralysis), endocrinologists (in the case of diabetes or thyroid/parathyroid gland disorders) and gynecologists (when menacing) may be needed. If foot curvature appears to the background of osteoporosis, densitometry is required - a study of bone density.
Treatment
Some of the main methods of treating foot valgus, conservative and operating curvature are distinguished. Do not destroy sore joints with ointment and injection!
A conservative approach
This type of help is intended to get rid of the symptoms of the disease, but does not eliminate the cause of the pathological root.
This technique includes:
- Use of orthopedic insoles to support plus bones, foot gates, as well as the removal of valgus lesions in the middle and back of the foot;
- Taping - Repair your feet and ankles using a special adhesive ribbon with the right elasticity. Tape tape is worn around hours within 3-5 days, after which they are replaced;
- Orthopedic shoes sewing by individual standards;
- The use of orthosis and other setting devices on the feet and ankles.
Conservative methods also include physiotherapy procedures (ozokerite, paraffin applications, electrophoresis, magnetic effects), massage and physiotherapy training complexes, developed for specific clinical cases. Be careful! Today, most experts prefer treatment surgery, as conservative therapy is ineffective (according to statistical, it is not useful in 60% of cases).
Surgical intervention
The amount of operation and its type depends on the direct stage of the disease. Therefore, the first stage of the deformation of the valgus is treated by synovectomy (removal of the shell tendon for general tension correction) or osteotomy (surgery) heel to return to the correct anatomy position. In the second stage of the development of the disease, the transfer of finger tendons is used. Such interventions are usually performed on the background of heel surgery or dried arthrodesis (ram's surgical surgery between ram and scaphoids).
Degree curvature III requires arthrodesis several foot joints at once: free-free, five-cup-cubic and ram-deheed. Three immobilization occurs are often equipped with heel surgery. At the pathological stage of IV, reconstructive operations are required not only on the feet, but also on the ankle. In this case, the instability of the ligaments is adjusted using the transfer (from their own body or artificial material). The number of operations on the foot itself is the same as the level of curvature III.
A period of recovery
Recovery includes walking without support on the feet operated for 2 months. At the same time, patients should wear removable gypsum gypsum from 1. 5 to 3 months. The active movement of the footed foot is recommended to begin after 1. 5 months after surgery. By the 3rd month, the Physical Education Strengthening Complex was introduced. However, the patient is then prohibited from walking and active sports activities. Keep in mind that it is possible to evaluate the final results of the surgery just six months later.
Precaution
Prevention of Deformation Valgus stops including the following steps:
- Early correction of congenital anomalies with improper bone arrangement from the feet or shortening of tendon grains (vertical bone bones, short heel tendons);
- Correction of posture disorders (scoliosis, etc. );
- Timely traumatic lesion treatment (bone fractures, lower legs, thighs or knee joints, ligaments and tendons);
- Proper recovery after paralysis (immobilization) due to damage to the nervous system for encephalitis, polyomyelitis, stroke, cerebrospinal root violation for hernia, and so on;
- The release of cramps (persistent reduction) of lower leg muscles;
- Therapy for joint disease: bone system pathology with vitamin D (rickets), diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis (reduction of bone density), impaired function of the thyroid gland and parathyroid, etc. ;
- Weight loss to normal (especially with weight gain in postmenopause or due to pregnancy);
- Selection of orthopedic shoes or use of supiners;
- The simple correction of the club without the treatment of "hyper-coincidence" leading to the secondary valgus that goes beyond the feet.
The prevention of the development of the disease is to use conservative methods and early reconstructive operations. In this case, physical activity is limited to prevent the destruction and curvature of ankle joints. Remember, the treatment at the same time about the deformation of the foot valgus not only improves the quality of life of the patient, but also prevents the development of osteochondrosis and arthrosis of the knee or hip!